How Structural Engineers Ensure Building Longevity
Buildings are expected to do far more than simply stand upright. They must withstand years of environmental stress, daily use, shifting soil conditions, and evolving safety standards. From residential homes to commercial skyscrapers, long-term performance depends on careful planning and precise execution long before construction begins. At the center of this process are structural engineers, whose expertise shapes how buildings respond to time, weather, and load demands.
Structural engineers combine physics, material science, and real-world experience to design frameworks that remain reliable for decades. Their work influences not only how long a building lasts, but also how safely and efficiently it performs throughout its life cycle. In this article, we explore the essential ways structural engineers contribute to building longevity and why their role remains indispensable in modern construction.
What Are the Key Responsibilities of Structural Engineers?
The responsibilities of structural engineers extend well beyond calculations and blueprints. At their core, they are responsible for ensuring that a structure can safely support all intended loads, including its own weight, occupants, furniture, equipment, and environmental forces such as wind and snow.
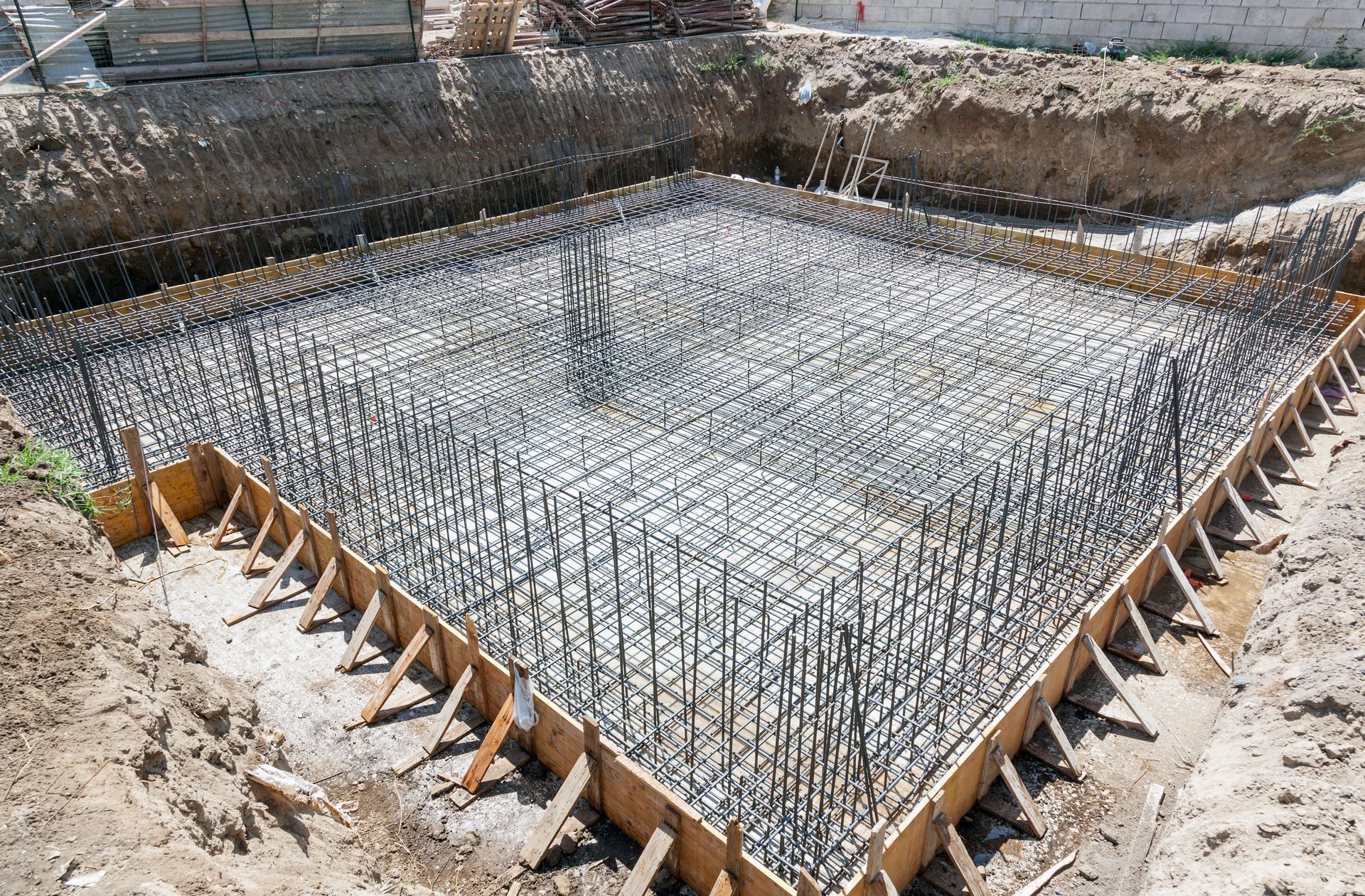
Early in a project, structural engineers evaluate site conditions, soil reports, and architectural plans to determine the most appropriate structural system. They design foundations, framing systems, beams, columns, and load paths that work together as a cohesive whole. These decisions directly affect how stress is distributed throughout the building, which plays a major role in preventing premature wear or failure.
Structural engineers also collaborate closely with architects, contractors, and other professionals to ensure that design intent aligns with construction realities. They review shop drawings, answer technical questions during construction, and verify that materials and methods meet required specifications. This oversight helps reduce errors that could compromise durability over time.
The scale of this responsibility reflects the size of the industry itself. According to IBISWorld, there are roughly 140,000 businesses operating within the engineering services industry in the United States, highlighting how essential engineering expertise has become across construction and infrastructure projects nationwide.
How Do Structural Engineers Select Materials for Durability?
Material selection is one of the most critical factors in building longevity, and structural engineers play a central role in making these choices. Every material behaves differently under stress, temperature changes, moisture exposure, and time. Selecting the right material for the right application can significantly extend a building’s usable life.
Structural engineers evaluate materials based on strength, flexibility, resistance to corrosion, and compatibility with environmental conditions. For example, steel may be favored for its high strength-to-weight ratio and flexibility, while reinforced concrete is often selected for its durability and fire resistance. In coastal or humid environments, engineers must account for corrosion risks and may specify protective coatings or alternative materials to prevent deterioration.
They also consider how materials interact with one another. Thermal expansion, moisture absorption, and chemical reactions can all affect long-term performance. By anticipating these interactions, structural engineers reduce the risk of cracking, warping, or material fatigue that can shorten a structure’s lifespan. These assessments help ensure that individual components function together as a stable, long-lasting system rather than wearing unevenly over time.
Cost considerations are part of the process, but durability often outweighs initial savings. A slightly higher upfront investment in resilient materials can prevent costly repairs or replacements decades later, reinforcing the long-term value of thoughtful engineering decisions. This long-range perspective supports buildings that remain reliable, safe, and efficient well beyond their original design expectations.
What Role Do Structural Engineers Play in Ensuring Safety During Earthquakes?
In seismically active regions, earthquake resistance is a defining factor in building longevity. Structural engineers design buildings not only to remain standing during seismic events, but also to minimize damage that could render them unsafe or unusable afterward.
Earthquake-resistant design focuses on flexibility and energy dissipation. Structural engineers incorporate features such as shear walls, moment-resisting frames, and base isolation systems that allow buildings to absorb and redistribute seismic forces. Rather than resisting movement entirely, these systems help structures move in controlled ways that reduce stress on critical components.
Engineers also analyze how buildings will perform under repeated loading cycles caused by aftershocks. This analysis helps prevent cumulative damage that might not be immediately visible but could weaken the structure over time. They often simulate various earthquake scenarios to understand how different magnitudes and directions of motion could impact structural performance.
By adhering to evolving building codes and applying advanced modeling techniques, structural engineers continuously refine seismic design strategies. Their work ensures that buildings remain safe and functional even after significant ground movement, contributing directly to long-term resilience and public safety. This proactive approach helps communities recover faster and reduces the likelihood of extensive repairs or rebuilding after major seismic events.
How Do Structural Engineers Integrate Sustainability Into Their Designs?
Sustainability and longevity are closely linked, and structural engineers play a key role in aligning these goals. A building designed to last longer naturally reduces the need for demolition, reconstruction, and material waste, making durability an essential component of sustainable construction.
Structural engineers support sustainability by optimizing designs to use materials efficiently without compromising strength. Advanced modeling allows them to reduce excess material while maintaining structural integrity. This approach lowers environmental impact while still supporting long-term performance.
They also contribute to adaptive reuse and flexible design strategies. By anticipating future changes in building use, structural engineers can design structures that accommodate renovations or expansions without major structural alterations. This adaptability extends a building’s relevance and usefulness across generations.
In addition, engineers increasingly incorporate low-carbon materials and design techniques that improve energy efficiency. Sustainable structural systems help buildings perform better over time while aligning with broader environmental goals, demonstrating how structural engineers support both durability and responsible development.
What Is the Importance of Regular Inspections Conducted by Structural Engineers?
Even the best-designed buildings require ongoing evaluation to maintain longevity. Regular inspections conducted by structural engineers are essential for identifying early signs of distress before they become serious problems.
During inspections, engineers assess foundations, load-bearing elements, and visible structural components for cracks, corrosion, settlement, or deformation. These evaluations help determine whether normal aging is occurring or if corrective action is needed. Early intervention can prevent minor issues from escalating into costly repairs or safety hazards.
Structural engineers also play a critical role following extreme events such as earthquakes, floods, or severe storms. Post-event assessments determine whether a building remains safe for occupancy and what repairs are necessary to restore structural integrity.
Routine inspections support proactive maintenance planning, allowing property owners to prioritize repairs and budget effectively. This ongoing relationship between structures and structural engineers ensures that buildings continue to meet safety and performance expectations throughout their lifespan.
Building longevity is not accidental. It is the result of careful planning, informed decision-making, and ongoing oversight carried out by skilled professionals. Through thoughtful design, strategic material selection, seismic planning, sustainable practices, and regular inspections, structural engineers safeguard the long-term performance of the built environment.
Their expertise ensures that buildings remain safe, functional, and resilient in the face of time and changing conditions. As construction demands continue to grow and evolve, the role of
structural engineers will remain central to creating structures that stand strong for generations to come. If you need an experienced engineer, reach out to the professional team at Jezerinac Geers & Associates, Inc today!









Share On: